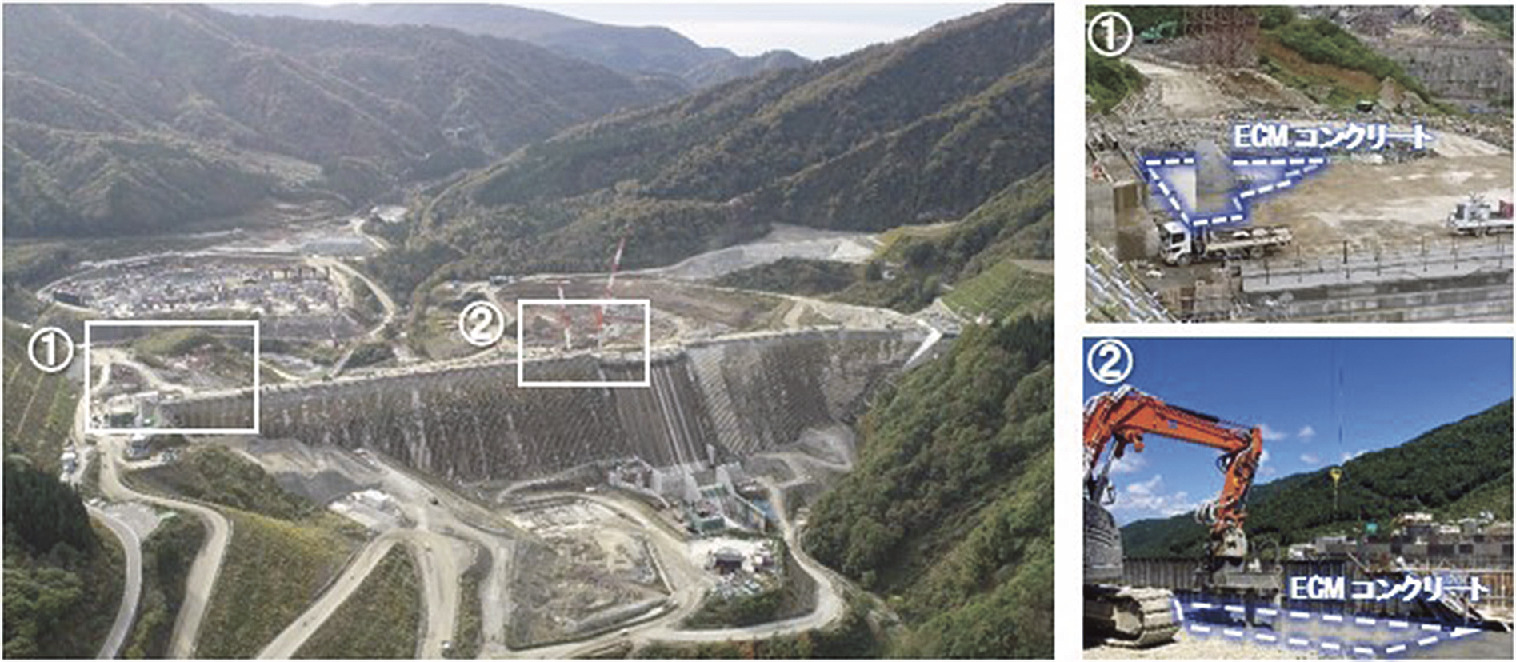
Japanese construction company Kajima Corporation has introduced its low-carbon ECM Concrete, which reduces carbon dioxide emissions during production, in the construction of Naruse Dam in Akita Prefecture. Commissioned by the Tohoku Regional Development Bureau of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport, and Tourism, the project utilized a total of 1,526 cubic meters of ECM Concrete for the dam’s body and part of the foundation reinforcement, achieving a reduction of 73 tons in CO₂ emissions. This marks the first large-scale application of ECM Concrete in a dam structure in Japan.
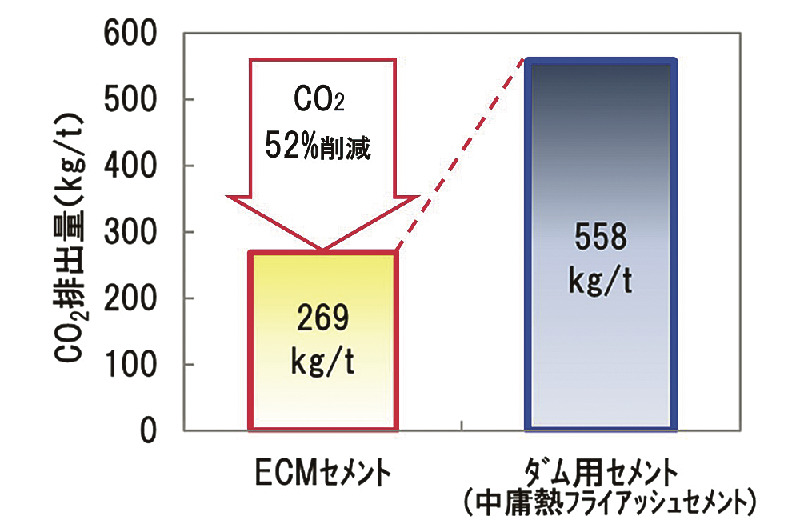
ECM Concrete is made using ECM Cement, which replaces 60–70% of ordinary cement with ground granulated blast-furnace slag. Compared to conventional cement, ECM Cement reduces CO₂ emissions during production by 52%. In this project, the 1,526 cubic meters of ECM Concrete were used for the dam body and the constructed rock concrete reinforcing the foundation bedrock. Testing confirmed that the peak internal temperatures of the ECM Concrete were on par with conventional concrete, ensuring high-quality performance.
Naruse Dam is designed as a trapezoidal-shaped CSG (cemented sand and gravel) dam, aiming to provide both flood control and water supply. It uses materials such as locally sourced soil, sand, and gravel mixed with cement and water. With a dam height of 114.5 meters, a volume of 4.85 million cubic meters, and a reservoir capacity of 78.5 million cubic meters, it is the largest trapezoidal CSG dam in Japan. The project is scheduled for completion by December 2026.
Kajima plans to expand the use of ECM Concrete and other environmentally friendly concrete in various structures, including concrete dams, to further promote sustainability in construction. (2024/12/04)